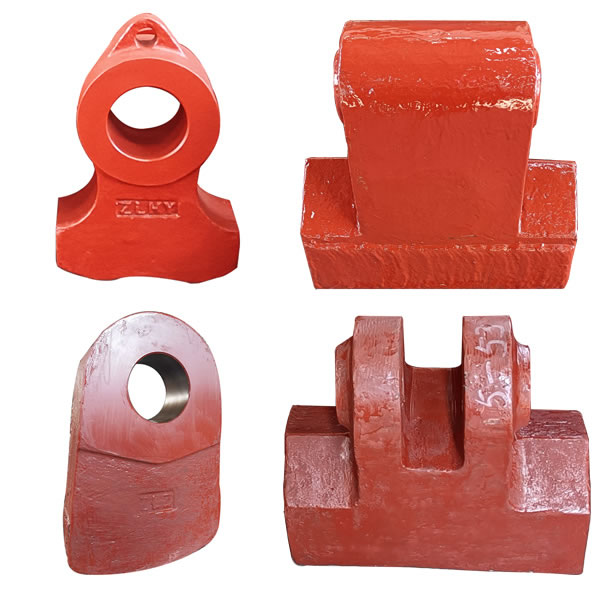
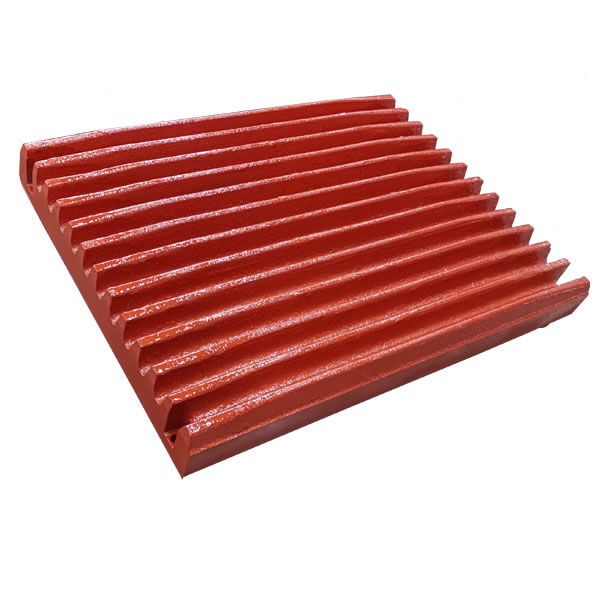
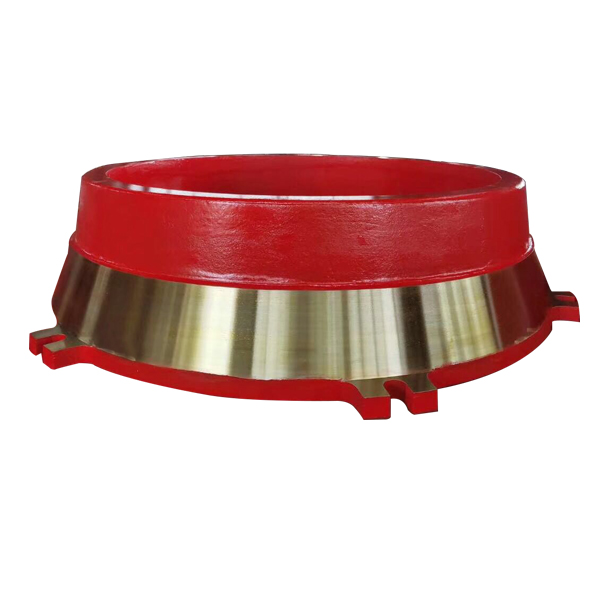
"For the same ball mill, why does the liner of plant A last for 2 years, but it is scrapped in 3 months in plant B?" A copper mining company chose the wrong liner material and processed high-hardness ore, and the annual loss cost surged by 2.17 million yuan. As a professional manufacturer with 30 years of experience in ball mill liner research and development, we deeply analyze the performance of 6 major mainstream materials to help you accurately match the working conditions, so that the liner life and production efficiency can be improved!
一、 "Performance Gene Map" of 6 Major liner Materials
1. High manganese steel liner (traditional overlord, being overturned)
Advantages:
✅ Excellent initial toughness (impact energy ≥ 150J)
✅ Affordable price
Disadvantages:
❌ Low hardness (HB170-230), fast wear rate
❌ Continuous impact is required to harden, and soft grinding conditions fail quickly
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ Strong impact crushing (such as initial crushing of granite)
⚠️ Use with caution: fine grinding section, low impact conditions, corrosive environment
2. High chromium cast iron liner (king of wear resistance, technology iteration)
Advantages:
✅ Ultra-high hardness (HRC58-62), wear resistance is 1-4 times higher than manganese steel
✅ Carbide network structure blocks wear path
Disadvantages:
❌ High brittleness (impact toughness ≤ 8J), easy to break
❌ Difficult to repair by welding, high maintenance cost
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ Medium and low impact fine grinding section (cement clinker, iron ore second stage grinding)
3. Rubber liner (silent guard, special working condition weapon)
Advantages:
✅ Noise reduction of 30dB, suitable for suburban factories
✅ Strong corrosion resistance (acid and alkali resistance pH3-11)
Disadvantages:
❌ High temperature difference resistance (>80℃ accelerated aging)
❌ Not suitable for large steel ball impact (ball diameter>60mm use with caution)
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ Wet grinding, fine grinding of chemical raw materials, environmentally sensitive areas
4. Ceramic composite liner (cutting-edge black technology, the first choice for high-end players)
Advantages:
✅ Hardness comparable to diamond (HV1200-1500)
✅ Zero metal pollution, suitable for high-purity materials such as lithium ore and quartz sand
Disadvantages:
❌ High unit price (about 4-6 times that of manganese steel)
❌ Poor thermal shock resistance (easy to crack when temperature difference > 200℃)
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ Ultrafine powder processing (above 325 mesh), food/pharmaceutical grade production line
5. Alloy steel liner (all-round warrior, large customization space)
Advantages:
✅ Strong adjustability (optimizing performance through Cr/Mo/V element ratio)
✅ High overall cost performance
Disadvantages:
❌ Long production cycle of non-standard parts (usually 15-30 days)
❌ Cost disadvantage of small batch procurement
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ Polymetallic mines, complex wear conditions
�� Our "working condition diagnosis service": free element ratio scheme
6. Bimetallic composite liner (rigid and flexible, solving industry problems)
Structural innovation:
▶ Surface layer: high chromium cast iron (2-3mm wear-resistant layer)
▶ Base layer: high-toughness low-alloy steel
Advantages:
✅ Impact resistance increased by 70%, wear resistance maintained at high chromium level
✅ Can be repaired by welding, and the operation and maintenance cost is reduced by 40%
Applicable scenarios:
⚙️ High impact + high wear "double high" working conditions (such as gold mine semi-autogenous mill)
二、 Golden formula for material selection: 4 steps to lock the best material
STEP 1 Diagnose working condition properties
Material hardness (Mohs hardness/Praetz coefficient)
Impact energy (steel ball diameter × mill speed)
Corrosive medium (pH value, sulfide content)
STEP 2 Quantify wear type
Chisel wear (>50%): Select high-toughness material
Fatigue wear: Prioritize hardness
Corrosive wear: Composite protection is required
STEP 3 Dynamic cost calculation
Total cost = purchase cost + number of replacements × (downtime loss + labor cost)
STEP 4 Adapt to special needs
Environmental protection requirements: rubber/ceramic
Product purity: non-metallic material
Installation restrictions: lightweight design
If you need help with material selection, please leave a message on the web page and our engineers will contact you as soon as possible!
Through precise material matching, every liner board becomes a profit growth point!